Introduction to Backup as a Service (BaaS)
Backup as a Service (BaaS) is a cloud-based solution that enables businesses and individuals to back up data remotely. Unlike traditional backup methods involving on-premise storage, BaaS providers manage the entire backup process—including storage, software, and security—in the cloud. This model offers greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. BaaS is particularly useful for disaster recovery, helping organizations avoid data loss due to cyberattacks, hardware failures, or natural disasters. By automating the backup process and reducing the need for manual intervention, BaaS minimizes downtime and ensures data integrity. With growing data volumes and evolving compliance regulations, BaaS is increasingly being adopted across industries as a modern data protection strategy. It serves as a critical component of any business continuity plan, particularly in a hybrid or fully remote IT environment.
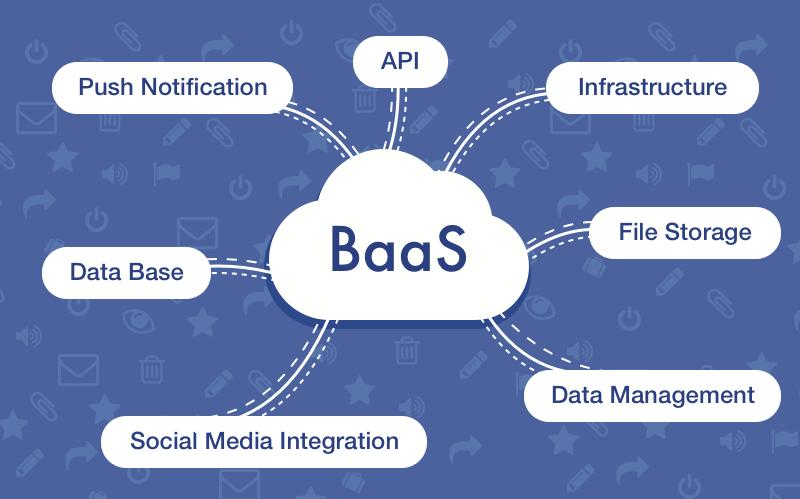
How BaaS Works and Its Key Components
Backup as a Service operates through a combination of client software, secure cloud storage, and a central management dashboard. Once configured, the software automatically backs up files, applications, or entire systems at scheduled intervals. These backups are encrypted during transfer and at rest to ensure data security. Most BaaS solutions offer incremental backups to save bandwidth and storage space by only capturing changes since the last backup. Centralized management tools allow IT administrators to monitor backup statuses, schedule tasks, restore data, and set compliance policies. BaaS supports multiple environments—on-premise, cloud-native, or hybrid—making it a versatile choice for enterprises. Key components include backup servers, secure cloud storage (often provided by hyperscalers like AWS or Azure), and retention settings that help organizations meet legal or operational data retention requirements.
Benefits of Using Backup as a Service
The advantages of Backup as a Service are numerous and align with modern IT needs. One of the most compelling benefits is reduced capital expenditure—organizations no longer need to invest in hardware, storage systems, or maintenance. BaaS is offered on a subscription model, making it more predictable and budget-friendly. It also offers high scalability, allowing businesses to increase or decrease storage capacity on-demand. With automated processes, human errors are minimized, and backups are consistently executed as scheduled. Additionally, BaaS enables rapid recovery of data, which is vital during ransomware attacks or system failures. Other advantages include centralized monitoring, compliance support, reduced IT workload, and faster deployment. Many services also offer versioning, allowing you to recover older file versions. These benefits collectively make BaaS an essential tool for modern data management strategies.
Top Use Cases for Backup as a Service
Backup as a Service is suitable for a wide range of use cases across various industries. For small and medium businesses (SMBs), it provides a cost-effective way to ensure data protection without requiring a dedicated IT staff. Enterprises often use BaaS for remote office backup, endpoint protection, and cloud application backup such as Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, or Salesforce. BaaS is also a key component in disaster recovery (DR) strategies, allowing businesses to recover critical systems quickly. Developers use BaaS to protect application data during continuous integration and deployment cycles. In regulated industries like healthcare and finance, BaaS helps organizations meet data retention and privacy regulations. Government agencies and educational institutions also leverage BaaS to safeguard public records and academic data. The service is highly adaptable, covering everything from file-level to full-system backups.
Challenges and Considerations in BaaS Adoption
While BaaS offers numerous advantages, it's important to be aware of potential challenges. One concern is data privacy—businesses must ensure that their BaaS provider complies with regional data protection laws such as GDPR or HIPAA. Latency can be another issue when restoring large volumes of data, especially with limited internet bandwidth. Cost management may become a concern if data volumes grow unchecked, as pricing is typically based on storage usage. Vendor lock-in is another risk, where businesses become dependent on a single provider’s ecosystem. To mitigate this, it's crucial to evaluate SLAs, support quality, backup frequency, encryption standards, and geographic data centers. Also, not all BaaS solutions support every application or operating system, so compatibility should be verified beforehand. Proper due diligence and vendor comparison are essential steps in ensuring successful BaaS implementation.
Future Trends in Backup as a Service
The BaaS market is evolving rapidly, driven by digital transformation, remote work trends, and growing cybersecurity threats. One key trend is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to optimize backup processes and predict failures. BaaS providers are increasingly offering ransomware detection and zero-trust architectures to enhance data security. There’s also a shift toward multi-cloud and hybrid backup strategies, enabling businesses to use several cloud providers to avoid vendor lock-in. Additionally, integration with DevOps tools and Kubernetes environments is becoming common, allowing for container-level backup and recovery. Another trend is the rise of BaaS tailored for SaaS applications, providing specialized protection for platforms like Microsoft 365 and Salesforce. As compliance becomes more complex, BaaS will play a greater role in data governance, audit readiness, and regulatory reporting.
Why BaaS is Critical for Modern Enterprises
In today’s digital-first world, data is one of the most valuable assets a company possesses. Backup as a Service offers a streamlined, secure, and scalable way to ensure that this data is protected against loss, corruption, and cyber threats. With automation, centralized control, and cloud-native architecture, BaaS aligns with modern IT infrastructure and business continuity goals. It reduces the burden on internal IT teams while delivering faster recovery and compliance support. Whether you’re an SMB looking for affordable backup or an enterprise in need of complex data protection, BaaS offers a solution that is both future-ready and cost-effective. As technology continues to evolve and threats grow more sophisticated, implementing a reliable BaaS solution is no longer optional—it’s a strategic necessity for operational resilience and long-term success.